Dial
control
| Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
| UI.Dial.new (x, y, size, value, min_value, max_value, rounding, start_value, markers, units, title) | Create a new dial.x and y are the coordinates where the dial will be displayed: numbersize is the size of the dial (default 22): numbervalue is the starting value: numbermin_value and max_value and the minimum and maximum values: numberrounding specifies the increments, and defaults to 0.01: numberstart_value sets where the fill line is drawn from, and defaults to 0: numbermarkers indicates where reference markers are to be placed on the dial: table of floats or integersunits will be displayed next to the value below the dial: stringtitle will be displayed instead of value and units below the dial: string |
| my_dial:set_value (number) | Set value : number |
| my_dial:set_value_delta (delta) | Set value using delta : number |
| my_dial:set_marker_position (marker_id, position) | Set marker positions : number |
| my_dial:redraw () | Redraw dial |
query
| Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
| my_dial.x | Returns originating x-coordinate : number |
| my_dial.y | Returns originating y-coordinate : number |
| my_dial.size | Returns size : number |
| my_dial.value | Returns dial’s current value : number |
| my_dial.min_value | Returns dial’s minimum value : number |
| my_dial.max_value | Returns dial’s maximum value : number |
| my_dial.rounding | Returns dial’s rounding value : number |
| my_dial.start_value | Returns dial’s start value : number |
| my_dial._markers | Returns marker positions : table |
| my_dial.units | Returns dial’s units : string |
| my_dial.title | Returns dial’s title : string |
| my_dial.active | Returns dial’s active state : boolean |
example
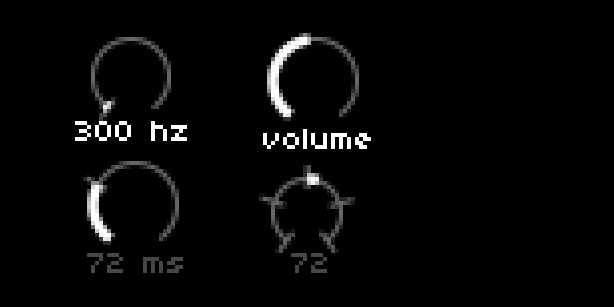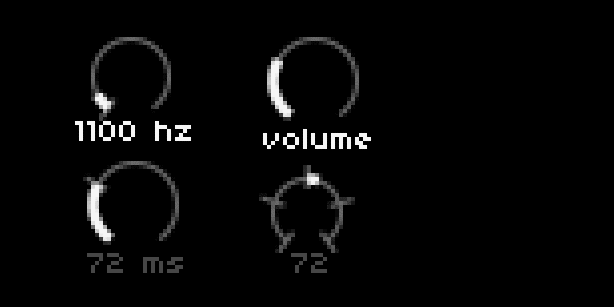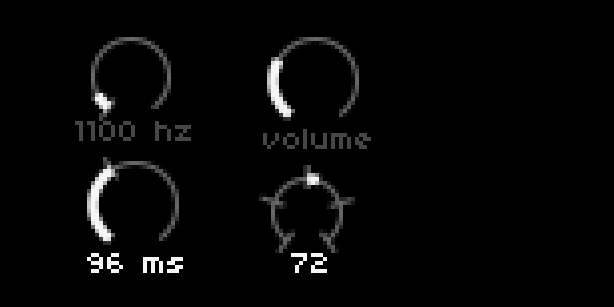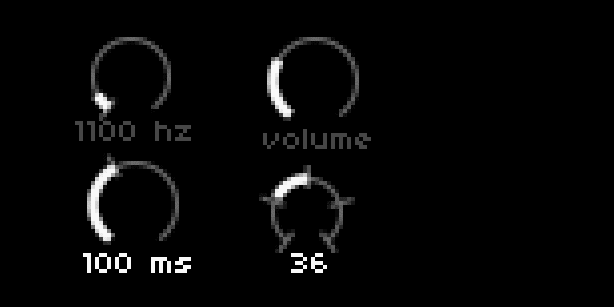
UI = require("ui")
dial = {}
active_row = 1 -- counter to indicate which row of dials is active
-- create 4 dials:
-- UI.Dial.new (x, y, size, value, min_value, max_value, rounding, start_value, markers, units, title)
dial[1] = UI.Dial.new(10, 3, 20, 300, 0, 12000, 100, 0, {0}, 'hz')
dial[2] = UI.Dial.new(55, 3, 22, 60, 0, 127, 1, 0, {},'','volume')
dial[3] = UI.Dial.new(10, 34, 22, 72, 0, 250, 1, 0, {72},'ms')
dial[4] = UI.Dial.new(55,38,18,72,0,127,1,64,{0,32,64,96,127})
-- set dial 3 and dial 4 to inactive
dial[3].active = false
dial[4].active = false
screen.aa(1) -- provides smoother screen drawing
function redraw()
screen.clear()
screen.fill()
-- dials need to be redrawn to display:
for i = 1,4 do
dial[i]:redraw()
end
screen.update()
end
function enc(n,d)
if n == 1 then
active_row = util.clamp(active_row+d,1,2)
-- select active row of dials
if active_row == 1 then
dial[1].active, dial[2].active = true,true
dial[3].active, dial[4].active = false,false
elseif active_row == 2 then
dial[1].active, dial[2].active = false,false
dial[3].active, dial[4].active = true,true
end
-- adjusting dial + marker values:
elseif n == 2 then
if dial[1].active then
dial[1]:set_value_delta(d*100)
else
dial[3]:set_value_delta(d)
dial[3]:set_marker_position(1,dial[3].value)
end
elseif n == 3 then
if dial[2].active then
dial[2]:set_value_delta(d)
else
dial[4]:set_value_delta(d)
end
end
redraw()
end
description
Draws a dial on the screen from the specified (x, y) pair. Size is determined by a single variable size and defaults to 22. Value is clamped to the dial’s min and max values and can be changed by direct assignment or incremental adjustment. The increments can be rounded by adjusting the float for rounding, which defaults to 0.01. The start_value sets where the fill line is drawn from, and defaults to 0. Reference markers can be added, in the form of a table of floats or integers. The dial can either display units next to the current value, or title instead of both value and units.